The following document was written by Mr Vik Veer MBBS(lond) MRCS(eng) DoHNS(eng) in Dec 2007. You may use the information here for personal use but if you intend to publish or present it, you must clearly credit the author and www.clinicaljunior.com
This site is not intended to be used by people who are not medically trained. Anyone using this site does so at their own risk and he/she assumes any and all liability. ALWAYS ASK YOUR SENIOR IF YOU ARE UNSURE ABOUT A PROCEDURE. NEVER CONDUCT A PROCEDURE YOU ARE UNSURE ABOUT.
Instruments used in ENT
This document is just a picture gallery of commonly used ENT instruments. This is particularly useful for those who wish to operate but need to know the names of instruments so that one can communicate effectively with other members of the theatre team. Also there is a station in the DOHNS exam that asks you to name various instruments - these are easy marks if you get in the habit of calling instruments by their proper names.

Xylocaine spray
Easy one to start with

Hydrogen Peroxide
Another easy one! Dilute with water (1:6 ratio) and gargle. Used to stop bleeding in cases of post tonsillectomy bleeds.

Lack Tongue Depressor
Obvious use

Silver Nitrate sticks
Used to chemically cautrise bleeding points. Below is a picture of the pack they come in


Catheter Clamp
Used to secure a catheter in the Post nasal space. See the epistaxis document for more details.

Thudicums Nasal Speculum
Used to examine the nose. Below is a picture of how they should be held


Fibreoptic Flexible Nasendoscope
Used to examine the upper airways. Note the arrows show that by pushing the lever the tip of the scope is turned in the vertical axis. You use this to direct yourself though the upper airways

Tongue Depressor
Obvious use.
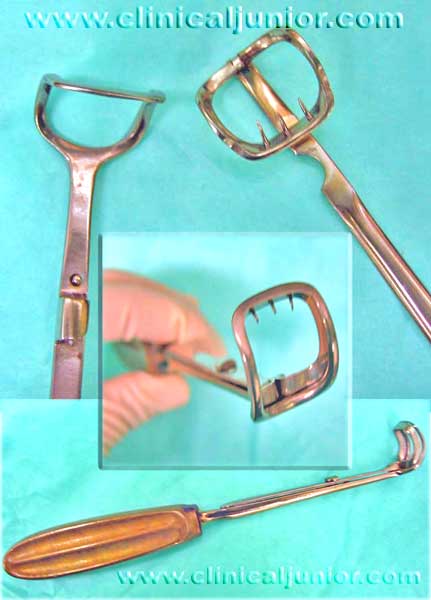
St Clair Thompson Adenoid Curette
Used to scrap off the adenoid out of the PNS. Note the gaurd with it's sharp teeth that most people avoid using now as it can traumatise the soft palate. Learn how to attach and remove the gaurd as it can come up in interview.
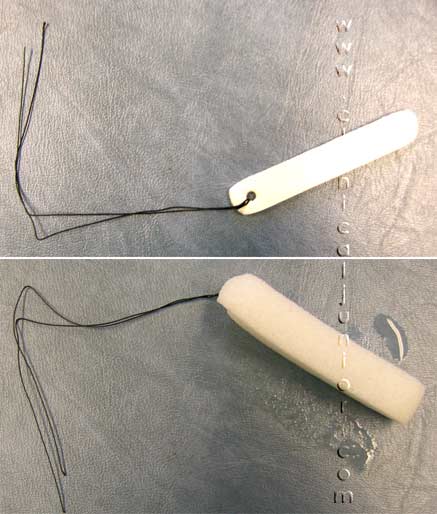
Merocel Nasal Pack
Used to pack the nose in epistaxis. Below is a picture of the packaging they come in


Yanker Sucker
Sucking up blood, etc.
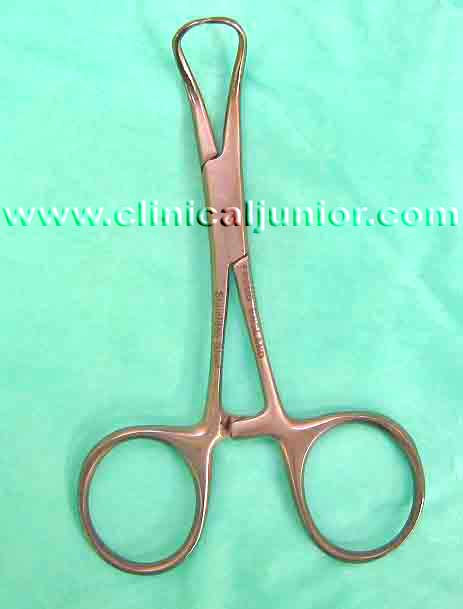
Boyle-Davis Gag
Used to keep the mouth open
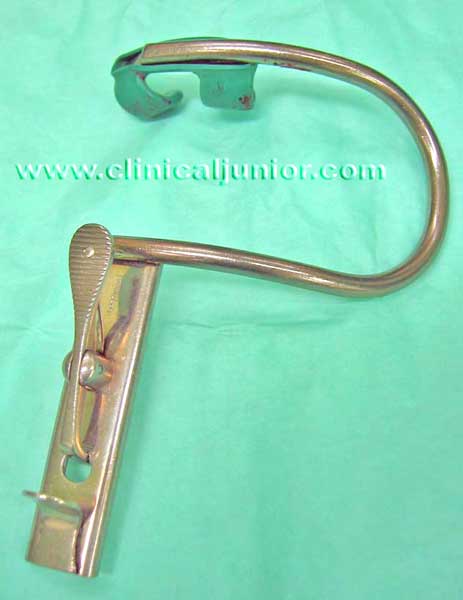
Theatre Drape Clip
Used to secure the drapes preventing them from falling off
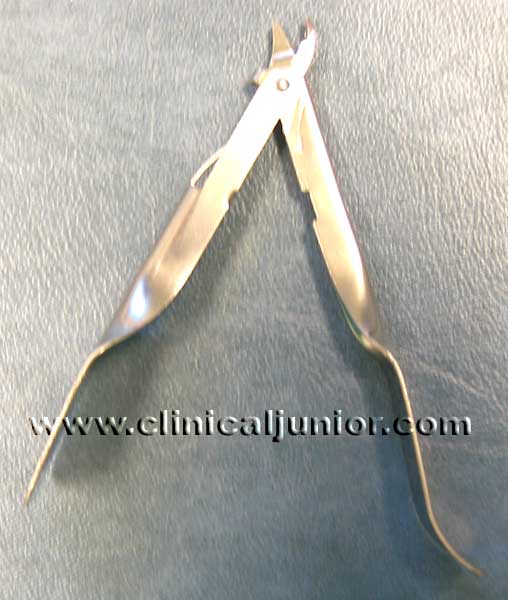
Staple Remover
Used to remove staples from the skin. Must have one of these by the bed of a Thyroidectomy patient post op as they may need the staples removed in an emergency to expel a haematoma.
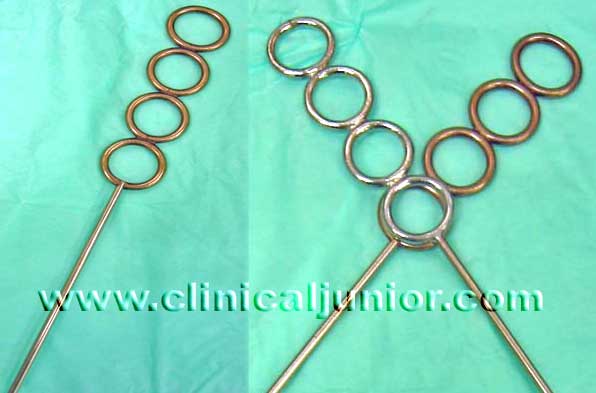
Draffin Rods
Used to prop up and secure a Boyle-Davis Gag or laryngoscopes so that you have two free hands to operate with. Two crossed rods are used either side of the neck to hold up the gag.
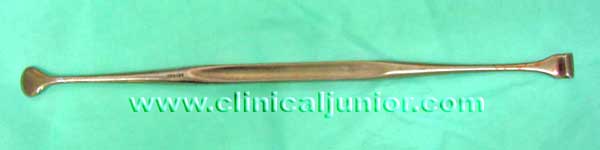
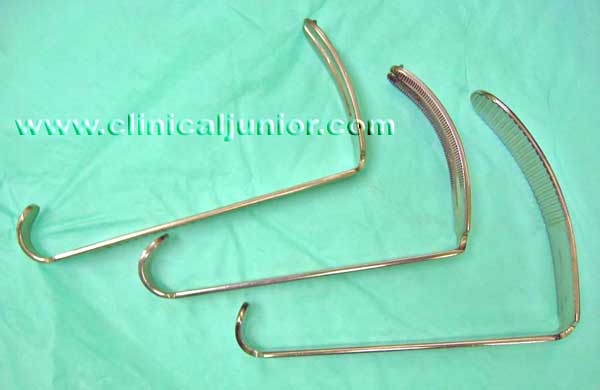
Mollison Pillar Retractor
Used to examine the tonsillar fossae after dissecting away the tonsils. The hook-like end is used to retract the superior pole anterior pillar and the flatter end is used elsewhere. Although in practice you can tailor it's use to the situation you are facing.

Eve Tonsil Snare
Used to remove the inferior pole of the tonsil having dissected away the other parts. A loop protrudes from the tip which encircles the inferior pole. Then you pull the loop back into the tip thereby dissecting the tonsil off cleanly. This instrument isn't used as much as in the past. Most people now tie off the inferior pole or dissect with bipolar to avoid the bleeding from the lingual tonsil which can be difficult to control.
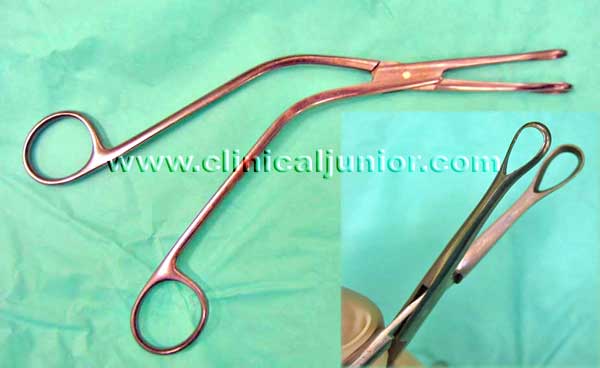
Denis Browne Tonsil Holding Forceps
Used to hold the tonsil while dissecting it
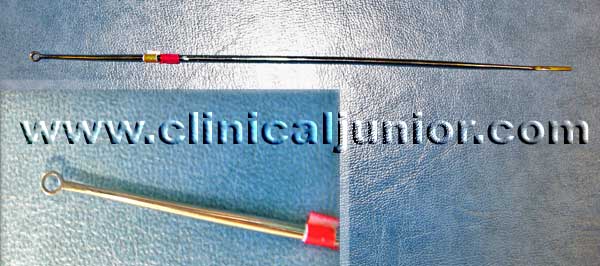
Jobson Horn Probe
Used to clean the external auditory canal
Daughty tongue blade
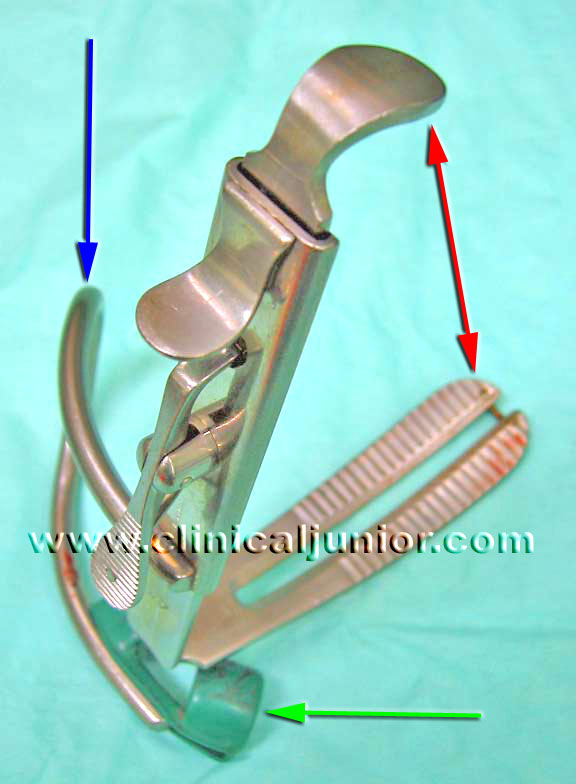
Used with a Boyle-Davis Gag to keep the mouth open. As you can see there are several different sizes to use for different sized mouths. Below is a picture of a blade and gag together. The red arrows point to the Daughty tongue blade. The blue arrow is to the Boyle-Davis Gag. The green points to the mouth gaurd on the Boyle-Davis Gag
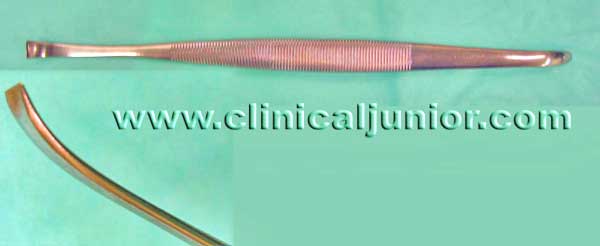
Gywnne Evans Dissector
Used to dissect away the tonsil from the fossa.
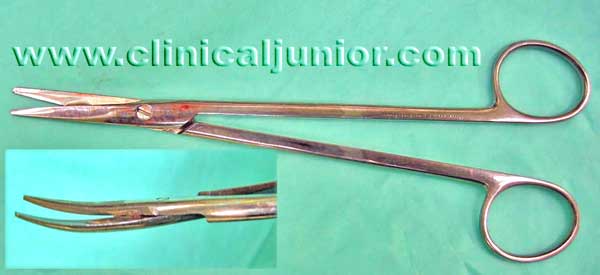
Curved Scissors
Used to dissect away the tonsil from the fossa. If there is a proper name for this please email me.
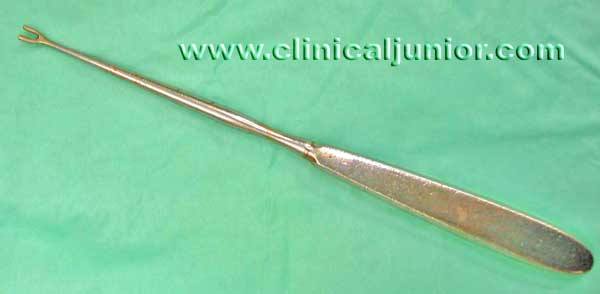
Negus Pusher
Used to tie a knot around the inferior pole of the tonsil. Quite difficult explain - so please watch a tonsillectomy to see how it is used.
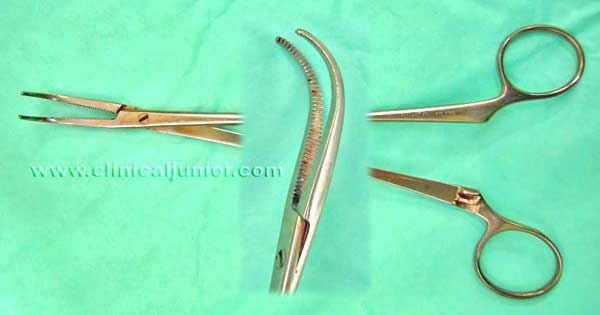
Curved Negus Tonsil Artery Forceps
Used to clamp the inferior pole of the tonsil just before removing it. It is left in place while a tie is knotted around it. Quite difficult explain - so please watch a tonsillectomy to see how it is used.
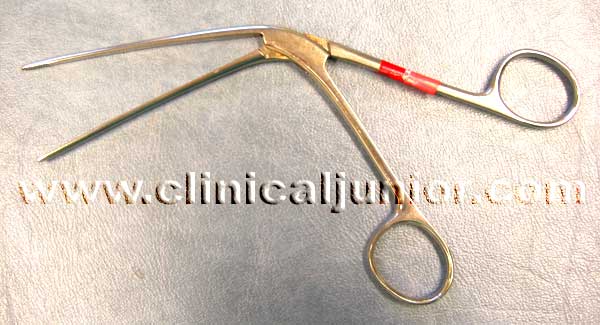
Tilley Nasal Dressing Forceps
Used to pack the nose with BIPP - see the epistaxis page.
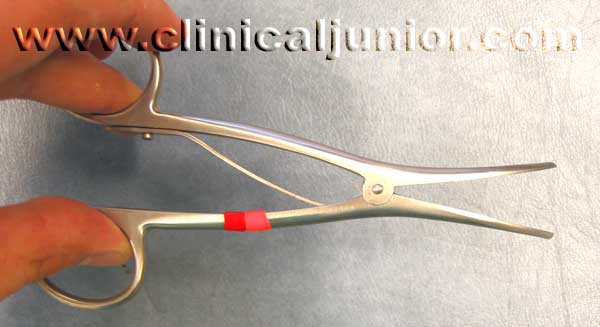
Trousseau Tracheal dilating forceps
Used to change a Tracheostomy tube
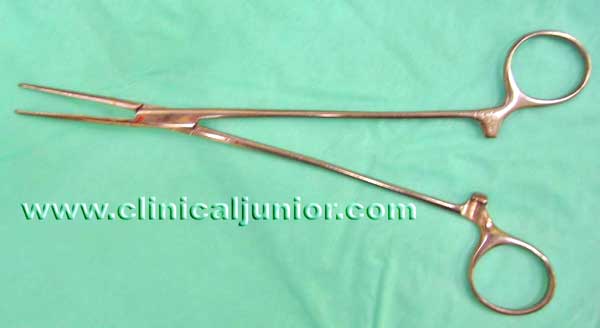
Birkett Forceps
Used mainly to clamp an arterial bleed and used in conjuction with a curved Negus to tie off the bleeder. Quite difficult explain - so please watch a tonsillectomy to see how it is used.
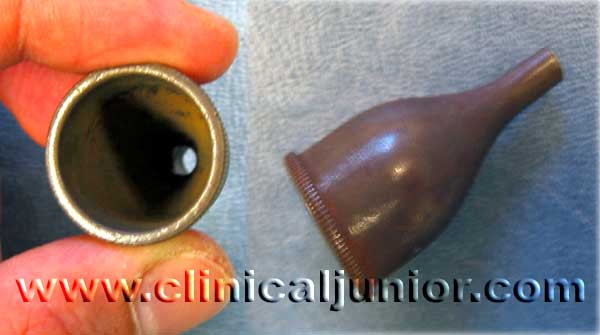
Gruber Aural Speculum
Used to examine the external auditory canal. There are loads of other types of speculum e.g. - Rosen Aural Speculum, Shea Aural Speculum, Toynbee Aural Speculum, Hartmann speculum, Tumarkin speculum etc.
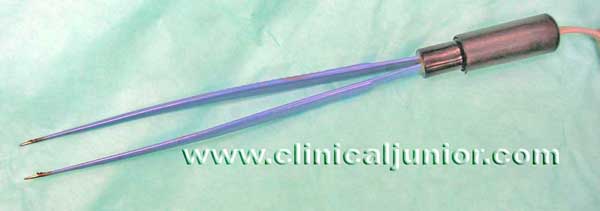
Bipolar forceps
Used to cautrise bleeding points and may be used to dissect tonsils away
There are clearly many many more instruments to be discussed. I will continue to update this section as i get photos of these instruments.