The following document was written by Mr Neela Mouli Doddi MBBS, MS(ENT), MRCS in Aug 08. You may use the information here for personal use but if you intend to publish or present it, you must clearly credit the author and www.clinicaljunior.com
This site is not intended to be used by people who are not medically trained. Anyone using this site does so at their own risk and he/she assumes any and all liability. ALWAYS ASK YOUR SENIOR IF YOU ARE UNSURE ABOUT A PROCEDURE. NEVER CONDUCT A PROCEDURE YOU ARE UNSURE ABOUT.
Stridor
It is a high pitched sound due to the turbulent flow of air through a partially obstructed airway.It should be distinguished from stertor and wheeze.
Stertor is an inspiratory sound resembling snoring, due to partial obstruction of the airway at the nasopharynx or oropharynx.
Stridor can be Inspiratory, Expiratory or both (biphasic).
Inspiratory stridor is common in supraglottic and glottic obstructions.
Expiratory Stridor occurs when the obstruction is in the smaller airways like bronchi, while biphasic stride occurs in lesions involving subglottis and trachea.
Common causes of stridor you are most likely to encounter during your on call
Adults
- Trauma to the airway
- Anaphylaxis
- Laryngeal oedema due to Epiglotitis, supraglotitis or laryngitis
- Neoplastic lesions of larynx
- Bilateral vocal cord paralysis
Children
- Laryngomalacia (usually in neonates and infants)
- Croup(laryngotracheobronchitis)( usually between 6 months to 2 years of age)
- Epiglotitis
- Inhaled foreign bodies
- Angeoneurotic oedema
Management in Adults
- Let the patient sit/lie down in the position he is most comfortable
- Give Oxygen or Heliox (mixture of 79%Helium and 21% Oxygen).
- Nebulised racemic adreneline
- Put an iv canula, give Dexamethasone or hydrocortisone iv
- Note the oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, pulse and blood pressure.
- Call the anaesthetist for help
- Keep the crash tracheostomy kit ready
- Call the ENT registrar
- Take a brief relevant history from the relatives or patient, keeping in view the common causes of stridor.
- Do arterial blood gases if possible
- When the stridor improves, do a flexible nasendoscopy (if you are not familiar with it, the ENT registrar would do it) to visualise the airway,thereby getting an idea about the cause for stridor.
- Organise AP and lateral X-rays of the neck and chest.
Management in Children
- Sit the child on mothers lap in a quiet room. Do not try to examine or cannulate or do anything that causes distress to the child as it would worsen the stridor.
- Call a senior paediatric consultant for help.
- Inform the ENT registrar.
- Monitor the respiratory rate . Monitor other vitals like oxygen saturations only if the child permits.
- It will be usefull if you could tell the Anaesthetist and the ENT registrar about the severity of stridor when you call for help. Severity of stridor can be assessed on inspection without disturbing the child by looking for tachypnoea, drooling of saliva, tracheal tug, intercostal indrawing on inspitation, respiratory effort, speech, cyanosis, level of consiousness and responsiveness.
Below are two pictures taken of common tracheostomy tubes, along with their main components.
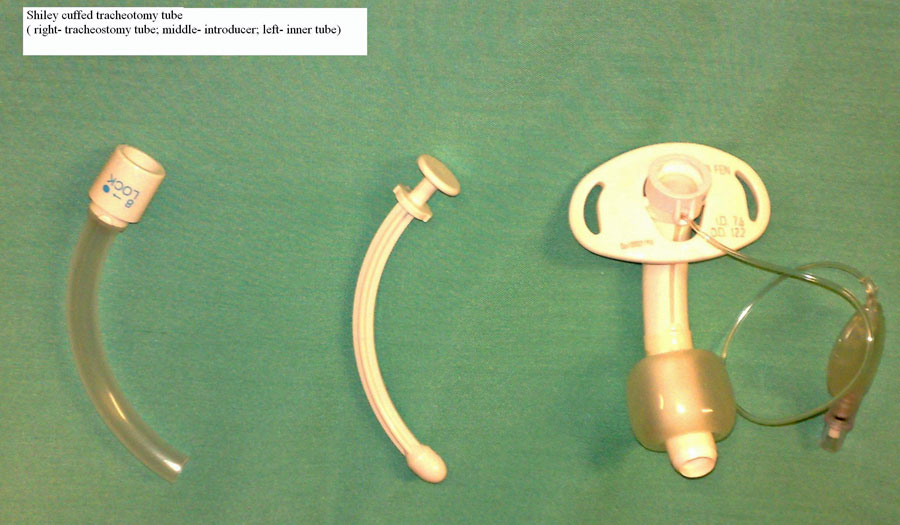
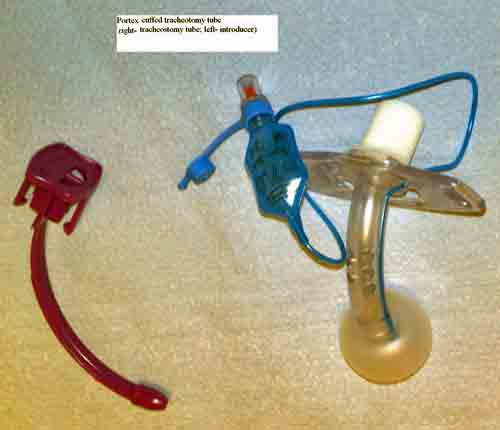
Further Reading
eMedicine - Stridor - by Brian Benson MD